What Civil War hero Joshua Chamberlain tells us about Buy-in
Buy-in occurs when your employees provide voluntary support.
A significant leadership challenge is gaining buy-in for a new initiative or one people previously opposed.
Buy-in explains the vital difference between high and low-performing organizations.
Without buy-in, leaders must focus on compliance, dispute resolution, and corrective action, which robs them of time and energy for strategy and growth. This disengagement tax is a hidden cost that drains revenue and undermines your business.
With buy-in, people do the right things in the right ways voluntarily, which frees leaders to focus on the future.
Joshua Chamberlain’s ability to gain buy-in saved the Union’s Army of the Potomac at Gettysburg, marking the beginning of the Confederacy’s end.
Two days before the battle, Chamberlain was ordered to guard 120 prisoners accused of desertion. They hailed from the 2nd Maine regiment. The accused believed they had signed two-year enlistments like others in the regiment, instead of three years, and wanted to return home with their comrades.
Chamberlain was given the authority to shoot them if necessary. He’d never be able to return home if he did. Guarding them would reduce his fighting force.
Chamberlain thought differently about the situation: what if they agreed to fight in our ranks for this massive battle?
Chamberlain’s regiment was down to about 250 soldiers. Adding 120 veteran fighters would strengthen his unit significantly.
Chamberlain focused on the three elements of buy-in: clarity on the mission and expectations for the upcoming battle, appeal to their self-interests of dignity, care, honor, and possibility of parole, and providing confidence in the way forward.
117 of the 120 deserters agreed to pick up their rifles and make the intrepid stand at Little Round Top. Without them, the 20th Maine would have been overrun, opening the entire flank of the Union army.
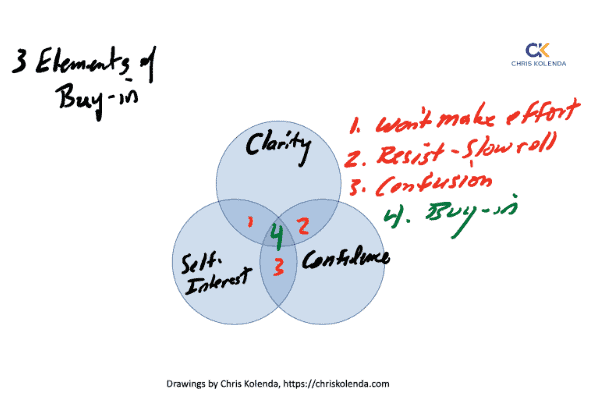
People buy in when they are clear about the expectations, believe they will be better off by adopting them, and are confident that the initiative or game plan will work.
People might be clear about an expectation and believe it may help them be better off, but won’t buy in without confidence that it will work. Mask fatigue during COVID is a recent example. Companies might believe that a new communications platform will help them be better off, but they won’t adopt it if they lack confidence in the technology or customer service.
By contrast, people can have clarity about a new idea and confidence it will work but won’t buy in if they believe they’ll be worse off. COVID vaccine resistance is a typical example. In your company, people who believe they are on the losing end will resist change. I find this to be the most common buy-in problem. The leaders are convinced everyone’s better off, but employees often find the talking points unconvincing. CNN’s recent employee revolt shows the perils of making changes that people believe leave them worse off.
Finally, employees can believe a particular change makes them better off and have confidence it will work, but will only buy-in for the common good if they are clear about the rationale and the details. Poor clarity results in silos or fiefdoms, where people adopt something good for them but detrimental to the company overall.
COVID protocols again offer a clear example of confusion, as medical expertise grew politicized and people believed only those who fit their pre-conceived beliefs. A client had challenges getting reports on time because employees did not understand the rationale. Once they gained clarity on that and how lateness was screwing other people, the reports arrived on time, regularly.
What are your biggest buy-in successes and challenges?
With so many businesses using flexible work locations, bringing people together for a substantive event that boosts cohesion and strengthens your foundation for growth is more important than ever.
A company off-site at a historical venue or national park allows you to create an experience that pays dividends for decades.
Let’s discuss some ideas if you want to do something special for your company.

 Photo by fauxels: https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-people-near-wooden-table-3184418/
Photo by fauxels: https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-people-near-wooden-table-3184418/