Create best value experiences: offer employees an EVP
Is your company trapped in the doom loop of high turnover, poor execution, and poor customer experience?
This loop leads to your customers seeking alternatives, which means declining sales, lower profits, and a higher risk of bankruptcy.
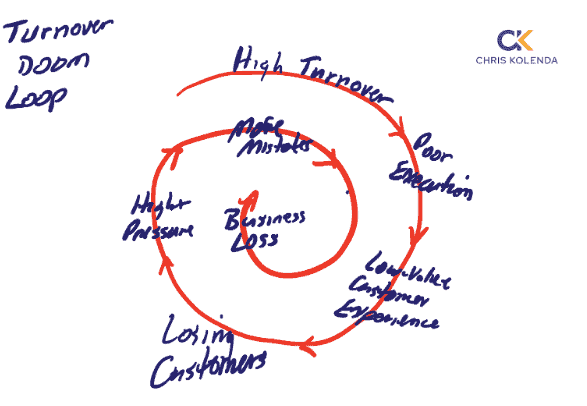
Organizations typically take their employees for granted, failing to invest in their well-being and future growth because they don’t see the payoff. A recent Harvard Business Review article shows the impact of this short-sighted approach.
People who feel unfulfilled and taken for granted tend to be on the lookout for a better fit. That means they are paying less attention to your company’s well-being because they are preoccupied with their own. It’s no wonder 69 percent of Americans report being unengaged at work.
People feeling undervalued jump ship. Losing people you’ve trained reduces productivity and heightens the likelihood of poor execution.
Poor execution damages your customers’ experiences, leading to more problems you need to fix. Unsatisfied customers will vote with their feet for a competitor.
Now you’re paying penalties on two levels.
First, losing existing customers undermines your business and makes you invest more heavily in attracting new customers (keeping existing customers tends to be cheaper than finding new ones).
Second, you get consumed in damage control. Instead of focusing on strategy, innovation, and growth (why you get paid X), you are cleaning up problems that a junior employee (who you pay Y) should have prevented in the first place.
X minus Y is your opportunity cost. If your salary is $250/hour and your employee’s is $50, your damage control costs you $200/hour.
[NOTE: Micromanaging has the same math.]
An employee value proposition (EVP) helps you reverse the spiral because your employees see how you are investing in them as people. A good EVP includes tangible and intangible benefits, both short and long-term.
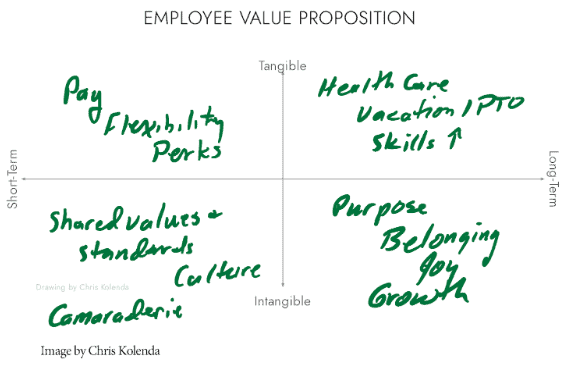
Many organizations focus on short-term tangible benefits, such as pay, and neglect the other three areas that emphasize purpose, belonging, and growth opportunities. Beyond a certain threshold, these factors are more prominent in stay-or-go decisions than pay.
Creating an EVP for your employees is an important forcing function that gets you to provide compelling, intangible benefits that will attract and retain the right people.
If this blog resonates with you and you are wondering about the next steps, Schedule a Call with Chris Kolenda.
 Photo by Andrea Piacquadio from Pexels: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-white-shirt-sitting-on-chair-3966781/
Photo by Andrea Piacquadio from Pexels: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-white-shirt-sitting-on-chair-3966781/ https://www.pexels.com/photo/crop-unrecognizable-female-psychologist-and-patient-discussing-mental-problems-during-session-7176319/
https://www.pexels.com/photo/crop-unrecognizable-female-psychologist-and-patient-discussing-mental-problems-during-session-7176319/ Photo by fauxels: https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-people-near-wooden-table-3184418/
Photo by fauxels: https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-people-near-wooden-table-3184418/

 Troubled Business Persons. Getty Images.
Troubled Business Persons. Getty Images. 
